Review Sheet Exercise 24 Special Senses Vision Answers
Special Senses Worksheet Answers
From WikiEducator
Jump to: navigation, search
1. The diagram shows an eye of a mammal. In the table below add the names of the structures indicated by the letters.
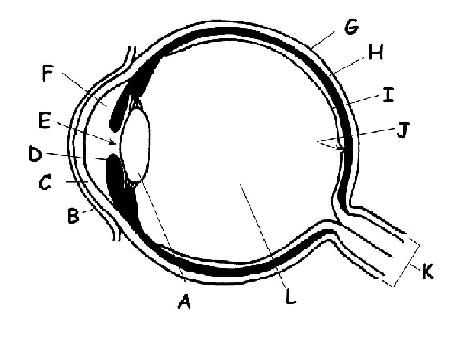
- CHOICES: Aqueous humour; choroid; conjunctiva; fovea; optic nerve; cornea; iris; lens; retina; sclera; vitreous sense of humour; educatee
| A | Lens |
| B | Conjunctiva |
| C | Cornea |
| D | Iris |
| E | Student |
| F | Anterior bedchamber |
| Grand | Sclera |
| H | Choroid |
| I | Retina |
| J | Fovea |
| Grand | Optic nerve |
| 50 | Posterior chamber |
2.Insert the correct term in the table below. Some terms may exist used more than than once.
- CHOICES: Aqueous humour; Choroid; Conjunctiva; Iris; Fovea; Optic nervus; Blind spot; Cornea; Sclera; Retina; Vitreous sense of humour; Pupil; Nictitating membrane
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Aqueous sense of humour | 1. Fluid that fills the anterior sleeping accommodation of the middle. |
| Sclera | ii. The white of the eye. |
| Fovea | 3. Area of the retina that lacks rods and cones. |
| Choroid | 4. Coating that provides nutrients to eye. Becomes the iris in the front of the eye. |
| Retina | 5. Layer containing the rods and cones. |
| Vitreous humour | half-dozen. Jelly-similar substance filling the posterior cavity of the eyeball. |
| Choroid | seven. Heavily pigmented coating that prevents light scattering within the eyeball: reflects light in nocturnal animals. |
| Iris | 8. Coloured structure that controls the size of the educatee. |
| Fovea | 9. Area of the retina of most detailed vision. |
| Cornea | 10. Most inductive part of the sclera—the window on to the earth. |
| Sclera | 11. Outer coating of tough, gristly connective tissue. |
| Pupil | 12. Discontinuity of the eye. Where the low-cal enters. |
| Conjunctiva | 13. The delicate membrane that covers the forepart of the eyeball. |
| Nictitating membrane | 14. The 3rd eyelid. |
| Optic nerve | 15. The nerve that takes nerve impulses from the retina to the brain. |
three. Are these statements about the middle true or false? If false give the correct respond.
- 1. Prey animals similar the rabbit take a large area of binocular vision. F Prey animals like the rabbit have a large expanse of monocular vision so they can see predators budgeted and only a small-scale area of binocular vision.
- 2. The rods of the retina function in dim light and practise not respond well to colour. T
- iii. The lacrimal glands secrete fluid that washes the outer surface of the eye and keeps it moist. T
- 4. The conjunctiva is the inner lining of the eyeball. F The conjunctiva is the fine membrane covering the cornea of the centre.
- 5. When the center focuses both the lens and the cornea change in shape. F Only the lens changes shape. The shape of the cornea is constant.
- 6. The cones of the retina are more than numerous in the region of the centre known every bit the fovea. T
- vii. Vitamin E is required in the diet to make the visual pigment plant in the cells of the retina. F vitamin A is the vitamin required to brand the visual purple of the sensory cells of the retina. It is found in carrots and greenish vegetables.
- 8. The size of the educatee changes in different light intensities. T
- ix. The parasympathetic nervous organization brings about dilation (widening) of the educatee. F The parasympathetic nervous system controls constriction of the pupil.
- 10. Nocturnal animals are normally colour-blind. T
4. Match the terms in the listing below to the descriptions in the table.
- A. Auditory ossicles; B. Pinna; C.Tympanic membrane; D. Cochlea; East. Ear canal; F. Eustachian tube; G. Vestibular organ; H.Middle ear I. Inner ear; J.Auditory nerve
| Term | Description |
|---|---|
| Eustachian tube | one. Connects the pharynx (throat)and the center ear to proceed the air pressures equal. |
| Tympanic membrane or ear drum | two. Vibrates as sound waves hit it. Transmits these vibrations to the auditory ossicles. |
| Ear pinna | 3. Animals can plough this towards the direction of the sound. |
| Auditory ossicles | iv. The smallest bones in the trunk. They transmit audio vibrations across the heart ear. |
| Cochlea | 5. Sound vibrations are converted here into electric impulses. |
| Vestibular organ | six. Contains receptors for the sense of balance and move. |
| Ear culvert | 7. This culvert can harbour mites in cats and dogs. |
| Inner ear | 8. The function of the ear consisting of the cochlea and vestibular organ. |
| Eye ear | 9. The part of the ear that contains the ear ossicles. |
| Auditory nerve | 10. The nerve that transmits nerve impulses from the cochlea to the brain |
5. The diagram beneath shows an ear of a mammal. Add together the labels below to the diagram.
- Auditory ossicles; Pinna; Tympanic membrane; Cochlea; Ear canal; Eustacian tube; Semicircular canals; Outer ear; Middle ear; Inner ear; Auditory nerve
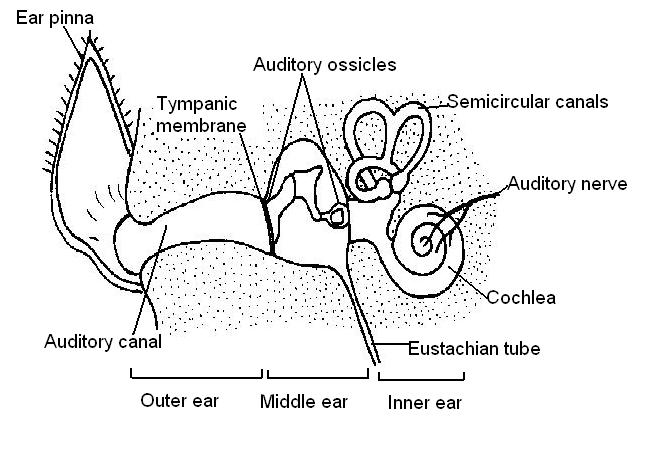
6. Rearrange these parts of the ear in the order in which sound waves travel to stimulate the cochlea.
- Auditory ossicles; Tympanic membrane; Ear canal; Inner ear
| Sound | Ear canal | Tympanic membrane | Auditory ossicles | Inner ear | Cochlea |
|---|
7. Complete the statements beneath by calculation the words in assuming.
tongue; temperature; otoliths; olfactory; hairs; olfactory organ; pressure; vestibular; touch; cerebellum; semicircular canals
-
- At that place are two parts to the vestibular organ. The first office consists of the semicircular canals which respond to changes in speed and management of movement of the body.
- The canals are filled with fluid and fine hairs that are stimulated when the head moves.
- The receptor cells ship nerve impulses along the vestibular nerve to the cerebellum in the brain.
- The otolith organs form the second function of the vestibular organ. They contain tiny pieces of chalk chosen otoliths that stimulate hair cells and tell the brute which way upwards it is.
- The special sense organ for taste are located on the tongue.
- The sensory cells concerned with smell are called the olfactory organ. This is located in the nose.
- In the pare, cells that sense temperature, pressure and bear upon are found.
Render to Special Senses Worksheet
Return to WikiEducator Anatomy and Physiology of Animals
medinasposeen1955.blogspot.com
Source: https://wikieducator.org/Special_Senses_Worksheet_Answers
0 Response to "Review Sheet Exercise 24 Special Senses Vision Answers"
Post a Comment